Restore Your Confidence, One Follicle at a Time Hair Transplantation
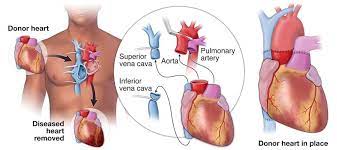
A heart transplant is a complex surgical procedure that involves replacing a diseased or damaged heart with a healthy heart from a donor. This article provides an overview of heart transplantation, including its indications, procedure details, recovery, risks, benefits, and outlook for recipients.
A heart transplant is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a diseased or failing heart with a healthy heart from a donor. It is typically considered a last-resort treatment for individuals with end-stage heart failure, where other treatments have been ineffective in improving heart function.
Following hair transplant surgery, patients may experience tenderness and discomfort. Pain medication and bandages are typically prescribed to alleviate discomfort and promote healing. While initial hair shedding may occur within a few weeks, new hair growth should become noticeable within a few months. Significant results are often observed after 6 to 9 months of the procedure.
Heart transplantation is recommended for individuals with end-stage heart failure, characterized by permanent damage or weakness in the heart that impairs its ability to pump blood effectively. Common conditions that may lead to end-stage heart failure include cardiomyopathy, coronary artery disease, congenital heart disease, and valvular heart disease.
Before a heart transplant, patients undergo a thorough evaluation to assess their overall health and
suitability for the procedure. This evaluation includes medical, psychological, neurological,
dental, and social assessments. If deemed eligible, patients are added to the transplant waiting
list, where they receive bridge treatments to manage symptoms while awaiting transplantation.
During the heart transplant procedure, patients receive general anesthesia, and their heart is replaced with a donor heart. The surgery involves connecting the donor heart to the recipient's major blood vessels and ensuring proper blood flow. Following the procedure, patients undergo a period of hospital recovery, typically lasting one to three weeks.
Recovery from a heart transplant is a gradual process, with patients requiring ongoing medical care
and monitoring. Immunosuppressant medications are prescribed to prevent rejection of the donor
heart, and patients participate in cardiac rehabilitation programs to improve heart function and
overall health.
The outlook for heart transplant recipients has improved significantly in recent years, with high
survival rates reported post-transplant. While complications such as organ rejection, infections,
and graft failure are possible, advances in medicine and transplant care have contributed to
improved long-term outcomes for recipients.
Heart transplantation offers the potential benefit of extending and improving the quality of life for individuals with end-stage heart failure who have exhausted other treatment options. However, it is associated with risks and disadvantages, including the scarcity of donor hearts, the complexity of the surgical procedure, and the potential for complications such as organ rejection and infections.
 trasplantcost.com
trasplantcost.com
Our goal is to help patients feel good about our commitment to them, and that usually starts with helping them understand what they’ll go through.
Location, City, Mumbai
info@Transplantcost.com
+91 888 983678
© Info@Transplantcost.com. All Rights Reserved.